A pipe operates at steady-state, steady-flow conditions. Steam enters the pipe at 300°C and 250 kPa, and exits at 250°C and 200 kPa. The volumetric flow rate of the steam entering the pipe is 1.2 m3/s. Assume that there are no work interactions.
(a) Determine the heat transfer rate to or from the pipe.
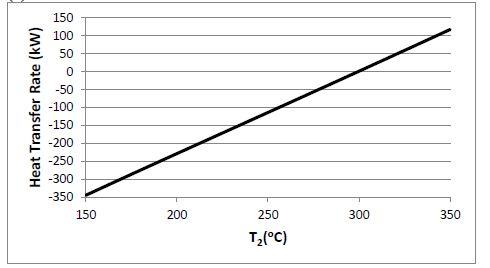
(b) Using your equations, plot the rate of heat transfer for the same inlet conditions and outlet pressure, but for outlet
temperatures varying from 150°C to 350°C.
Given: V?1 = 1.2 m3/s; T1 = 300°C; P1 = 250 kPa; T2 = 250°C; P2 = 200 kPa
Steady-state, steady-flow; (Inlet = State 1; Outlet = State 2)
Assume: W?= 0 ; neglect changes in kinetic and potential energy
What will be an ideal response?
(a) For a single inlet, single-outlet, steady-state, steady-flow device:
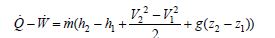
With no power, and no changes in kinetic and potential energy:
Q? = m? (h2 ? h1)
The mass flow rate can be found from the volumetric flow rate of the inlet:
m? =V?1/v1
The specific volume of the inlet, and the enthalpy values of the inlet and outlet can be found with on-line property program:
v1 = 1.0517 m3/kg
h1 = 3070.85 kJ/kg
h2 = 2971.26 kJ/kg
So, m? = (1.2 m3/s) / (1.0517 m3/kg) = 1.14 kg/s
Q? = (1.14 kg/s)(2971.26 – 3070.85)kJ/kg = -114 kW
(b)
You might also like to view...
The ____________________ period is the time during which the animal is pregnant
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The heptatitis A virus causes hepatitis, a disease of the:
a. liver c. lungs b. heart d. brain
In an animal's cell, fewer molecules of oxygen are inside the cell than outside the cell
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Vendor A supplies parts, each of which has probability 0.03 of being defective. Vendor B also supplies parts, each of which has probability 0.05 of being defective. You receive a shipment of 100 parts from each vendor.
a. Let X be the number of defective parts in the shipment from vendor A and let Y be the number of defective parts in the shipment from vendor B. What are the distributions of X and Y? b. Generate simulated samples of size 1000 from the distributions of X and Y. c. Use the samples to estimate the probability that the total number of defective parts is less than 10. d. Use the samples to estimate the probability that the shipment from vendor A contains more defective parts than the shipment from vendor B. e. Construct a normal probability plot for the total number of defective parts. Is this quantity approximately normally distributed?