Firms are often more efficient than markets as coordinators of economic activity because
A) firms can achieve lower transaction costs.
B) markets cannot coordinate production.
C) firms don't rely on economies of scale while markets do.
D) firm coordination is always more economically efficient than market coordination.
A
You might also like to view...
The quantity theory of money and prices assumes
A) the price level is increasing at a constant rate. B) the price level is constant. C) real output is constant. D) velocity is constant.
In the Keynesian framework, as long as output is ________ the equilibrium level, unplanned inventory investment will remain negative and firms will continue to ________ production
A) below; lower B) above; lower C) below; raise D) above; raise
The economy is viewed as operating at full employment:
a. when there is no frictional unemployment. b. when there is no structural unemployment. c. when there is no seasonal unemployment. d. when there is no cyclical unemployment.
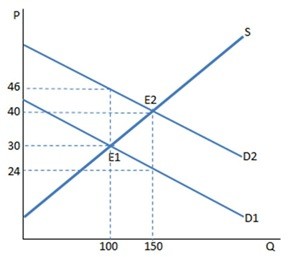 The graph shown portrays a subsidy to buyers. The subsidy causes:
The graph shown portrays a subsidy to buyers. The subsidy causes:
A. 50 more units to be sold in this market. B. 100 fewer units to be sold in this market. C. 50 fewer units to be sold in this market. D. 150 more units to be sold in this market.