Explain and describe the five primary tastes. Focus on the location of the taste buds on your tongue and the chemicals they can sense
What will be an ideal response?
(1 ) Sweet: indicates the item is loaded with carbohydrates that can be used as calories and energy within the body. The tip of the tongue is most sensitive to sweet tastes. (2 ) Taste buds most sensitive to salt are located along the sides of the tongue. Salty items can be used to replace electrolytes lost through exercise and perspiration. (3 ) A sour taste is usually associated with food items that haven't fully ripened and would be better eaten later. Citrus fruits are sour but are good sources of vitamin C and other antioxidants. Sour taste is associated mostly with the sides of the tongue. (4 ) Bitter tastes are normally associated with foods that are poisoned or spoiled. Bitter taste is associated with the back of the tongue. (5 ) Umami detects the presence of amino acids, small proteins, and nucleotides. Taste buds that detect umami are distributed toward the back of the tongue and throughout.
You might also like to view...
The multiple effects of a single gene on the phenotype of an organism is called _______
A. epistasis B. penetrance C. expressivity D. overdominance E. pleiotropy
Referring to the figure, an average bacterium is roughly the same size as which eukaryotic organelle?
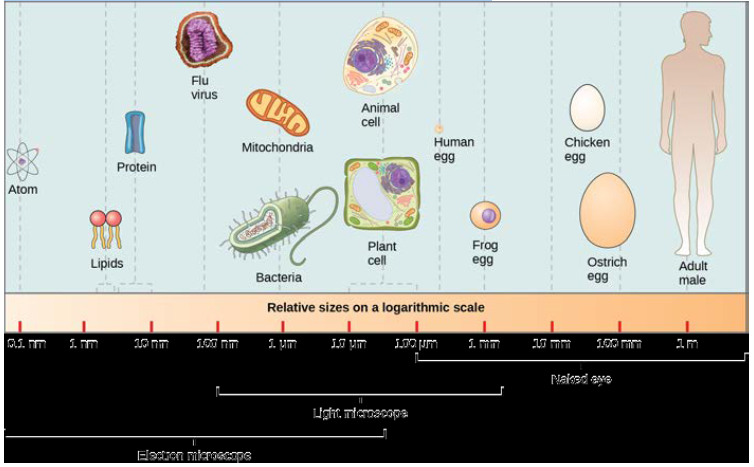
a. lipid
b. protein
c. mitochondria
d. egg
Proteins function ____
a. as energy carriers b. as the ‘backbone’ of the DNA molecule c. as component parts of enzymes d. in energy storage within the cell nucleus e. in transmission of genetic information
The structures in the outermost ring of floral structures that cover and protect the bud are
A. receptacles. B. sepals. C. stamens. D. carpels. E. petals.