In short-run equilibrium, a perfectly competitive firm
a. may earn a profit or a loss.
b. always earns a profit.
c. never earns a profit.
d. earns a profit only if the firm has no fixed cost.
a
You might also like to view...
Suppose that all workers place a value on their leisure of 75 goods per day. The production function relating output per day Y to the number of people working per day N is
Y = 500N - 0.4 N2, and the marginal product of labor is MPN = 500 - 0.8 N. A 25% tax is levied on wages. (a) How much is output per day? (b) In terms of lost output, what is the cost of the distortion introduced by this tax?
When the federal government installs a price support program that requires the government to purchase all of a good not bought in the private economy at the support price, the impact on total welfare is the
A) change in consumer surplus. B) change in consumer surplus + the change in producer surplus + the cost to government. C) change in consumer surplus + the change in producer surplus - the cost to government. D) change in consumer surplus + the change in producer surplus.
If a natural disaster were to cause a negative long-run supply shock to the economy, once the economy adjusts, the new equilibrium will be at a:
A. higher price level and lower level of output. B. lower price level and lower level of output. C. higher price level and higher level of output. D. lower price level and higher level of output.
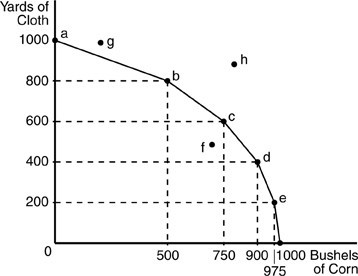 In the above figure, which of the following points indicates the efficient use of resources?
In the above figure, which of the following points indicates the efficient use of resources?
A. a B. f C. h D. g