With perfect price discrimination, a monopoly can extract the ________ price each customer is willing to pay and thereby obtain the entire ________ surplus
A) maximum; consumer
B) minimum; producer
C) maximum; producer
D) minimum; consumer
E) None of the above answers is correct.
A
You might also like to view...
Jack F. Altrades's decision whether to purchase a good from a firm or hire resources directly in the market will
a. depend, in part, on his production skill but not on his contract negotiation skill b. depend, in part, on the opportunity cost of his time but not on his skill c. not depend on the cost of identifying, measuring, and pricing inputs d. not depend on the cost of negotiating contracts e. depend, in part, on both his skill and the opportunity cost of his time
Explain the difference between the per se and "rule of reason" standards of the antitrust laws
In order to demand a good, the buyer must:
a) Want the good very much. b) Think that the good has significant utility. c) Be aware of the opportunity costs. d) Be both willing and able to pay for it.
Exhibit 8-2 Consumption function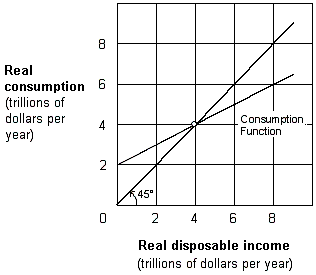
A. autonomous consumption. B. real consumption spending. C. real disposable income. D. all points where real consumption equals real disposable income.