A 6.0-kg object moving 2.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional elastic collision with a 4.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. What is the total kinetic energy of the two-mass system after the collision?
A. 30 J
B. 62 J
C. 20 J
D. 44 J
E. 24 J
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A supercluster is a cluster of supergiants
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Electric Field Lines: Two stationary point charges q1 and q2 are shown in the figure along with a sketch of some field lines representing the electric field produced by them. What can you deduce from the sketch?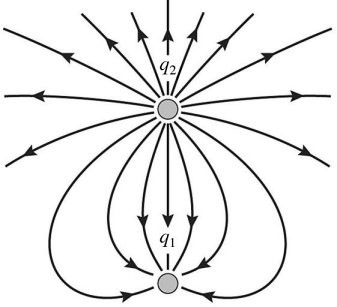
A. q1 is negative and q2 is positive; the magnitudes are equal. B. q1 and q2 have the same sign; the magnitudes are equal. C. q1 is positive and q2 is negative; the magnitude of q1 is greater than the magnitude of q2. D. q1 is negative and q2 is positive; the magnitude of q1 is less than the magnitude of q2. E. q1 and q2 have the same sign; the magnitude of q1 is greater than the magnitude of q2.
A 4.00 kg mass is moving at 4.00 m/s 45.0 degrees NORTH of WEST and a 6.00 kg mass is moving at 3.00 m/s 30.0 degrees SOUTH of EAST . The velocity of the center of mass is (a), and the velocity NORTH of the center of mass is (b)
A. a = 0.430 m/s, b = 2.30 m/s. B. a = 1.23 m/s, b = 0.230 m/s. C. a = 0.430 m/s, b = 0.203 m/s. D. a = 1.73 m/s, b = 1.43 m/s. E. a = 0.430 m/s, b = 0.230 m/s.
The current I flowing in the wire
A. A B.B C.C