What is the equivalence principle of the general theory of relativity?
a. E0 = mc2.
b. Constant velocity is equivalent to a uniform gravitational field.
c. Gravitational potential energy is equivalent to mass.
d. Constant acceleration is equivalent to a uniform gravitational field.
e. Any acceleration is completely equivalent to a uniform gravitational field.
d
You might also like to view...
Nuclear Binding Energy: The neutral 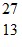 Al atom has a mass of 26.981539 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. What is the binding energy per nucleon for
Al atom has a mass of 26.981539 u; a neutral hydrogen atom has a mass of 1.007825 u; a neutron has a mass of 1.008665 u; and a proton has a mass of 1.007277 u. What is the binding energy per nucleon for 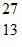 Al? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
Al? (1 u = 931.5 MeV/c2)
A. 8.3 MeV B. 6.7 MeV C. 5.4 MeV D. 3.4 MeV E. 2.8 MeV
A baseball player slides into third base. Why, according to the modern model of mechanics, does the player eventually come to rest?
A. All moving objects naturally come to rest eventually. B. Friction overpowers the force of the player’s motion. C. The force of the player’s motion eventually wears out. D. A friction interaction changes the player’s motion. E. Other (specify).
Diffraction Gratings: The distance between the ruled lines on a diffraction grating is 1770 nm. The grating is illuminated at normal incidence with a parallel beam of white light in the 400 nm to 700 nm wavelength band. What is the longest wavelength that appears in the third order spectrum?
A. 590 nm B. 570 nm C. 550 nm D. 530 nm E. 610 nm
Global climate change has been suggested as a reason for societal changes or collapses in several instances. Why should drought or other climate-induced change cause social change? Explain how this could possibly occur
What will be an ideal response?