The ability to produce a good at lower opportunity costs than another producer is known as
A) comparative advantage.
B) marginal cost production.
C) economies of scale.
D) absolute advantage.
A
You might also like to view...
Refer to the above figure. A price control has been set which has led to a surplus. This means that a
A) price ceiling has been set at P1. B) price floor has been set at P1. C) price ceiling has been set at P2. D) price floor has been set at P2.
You have a bond that will pay you one hundred dollars one year from today. If the prevailing interest rate is r, the bond is currently worth
a. 100/r b. 100r c. 100/(1 + r) d. 100
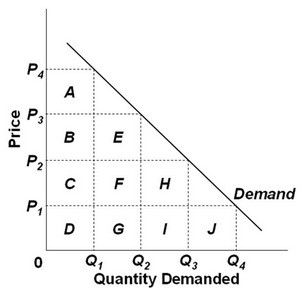 Refer to the graph above and assume that the areas of the boxes are the same. Consider a situation where price decreases from P2 to P1. In this price range, demand is relatively:
Refer to the graph above and assume that the areas of the boxes are the same. Consider a situation where price decreases from P2 to P1. In this price range, demand is relatively:
A. inelastic because the gain in total revenue (area J) is less than the loss in total revenue (areas C + F + H). B. inelastic because the loss in total revenue (areas D + G + I + J) is greater than the gain in total revenue (areas C + F + H). C. elastic because the loss in total revenue (areas C + F + H) is greater than the gain in total revenue (area J). D. elastic because the loss in total revenue (area J) is less than the gain in total revenue (areas C + F + H).
Gross Domestic Product measures
A. the total market value of final goods and services produced within a nation's borders. B. the total worth of all goods consumed within the borders of a nation. C. the total income received by residents of a nation. D. the total value of labor used in the economy.