Refer to the accompanying figure. If demand shifts from D1 to D2, and at the same time, supply shifts from S1 to S2, then according to the figure: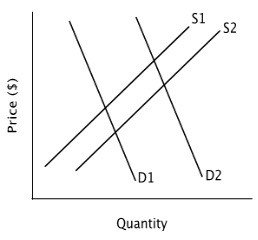
A. the equilibrium quantity will increase and the equilibrium price will decrease.
B. the equilibrium quantity will decrease and the equilibrium price will decrease.
C. the equilibrium quantity will decrease and the equilibrium price will increase.
D. the equilibrium quantity will increase and the equilibrium price will increase.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The price of a financial asset should equal the
A) present value of the payments to be received from owning the asset. B) future value of the payments to be received from owning the asset. C) face value of the asset less the future payments to be received from owning the asset. D) coupon value of the asset divided by the effective interest rate at the time the asset was purchased.
Properties of long-run competitive equilibrium with free entry include:
A. an equilibrium price equal to the minimum AC. B. firms earning zero profits. C. active firms producing at their efficient scales of production. D. All of these are properties of long-run competitive equilibrium.
The total of all planned expenditures in the entire economy is
A. aggregate demand. B. LRAS. C. aggregate supply. D. the open economy effect.
The post hoc, ergo propter hoc fallacy is the belief that
A. it is impossible to draw generalizations about cause and effect. B. what is true for a part is necessarily true for the whole. C. what is true for the whole is necessarily true of the parts. D. if Event A happens before Event B happens, then Event A causes Event B to occur.