Monopolies arise when there are
A) many substitutes but there are no barriers to entry.
B) no close substitutes and there are no barriers to entry.
C) no close substitutes and there are barriers to entry.
D) many substitutes and there barriers to entry.
E) None of the above answers are correct because the existence of a monopoly has nothing to do with the presence or absence of barriers to entry.
C
You might also like to view...
Refer to Goods X and Y. Suppose the consumer is spending all of his income buying some of both goods. If the marginal value of X is greater than the relative price of X, how can the consumer improve his level of satisfaction?
Assume that good X is on the horizontal axis and good Y is on the vertical axis in the consumer-choice diagram. PX denotes the price of good X, PY is the price of good Y, and I is the consumer's income. Unless otherwise stated, the consumer's preferences are assumed to satisfy the standard assumptions. a. By purchasing more of both goods. b. By purchasing more of good X and less of good Y. c. By purchasing more of good Y and less of good X. d. The consumer cannot improve his level of satisfaction because he is at the optimum.
Exhibit 7-12 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves
?
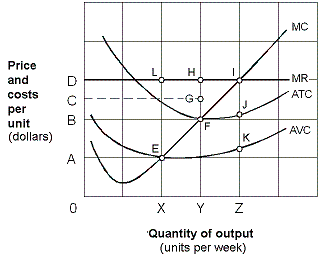
A. zero units of output because it is unprofitable. B. X units and incur a loss. C. Y units and break even. D. Z units and make an economic profit.
A tax wedge:
A. only occurs in markets when taxes are placed on large corporations. B. only occurs in markets when the tax is placed on buyers. C. refers to the difference in the price the buyer pays and the price the seller keeps. D. only occurs in markets when the tax is placed on sellers.
According to classical economists, a decrease in the rate of interest will
A. increase investment. B. increase consumer saving. C. increase the inflation rate. D. increase unemployment.