Suppose the labor market and all output markets are perfectly competitive. When the labor market is in equilibrium, the wage rate will:
A) be less than the marginal revenue product of labor.
B) equal the marginal revenue product of labor.
C) be greater than the marginal revenue product of labor.
D) None of the above is necessarily correct.
B
You might also like to view...
One thing that distinguishes normative economic principles from positive economic principles is that:
A. normative principles are pessimistic and positive principles are optimistic. B. normative principles tell us how people should behave, and positive principles tell us how people will behave. C. normative principles tell us how people will behave, and positive principles tell us how people should behave. D. normative principles reflect social norms, and positive principles reflect universal truths.
Refer to Figure 14-9. Uniguest, Inc is a company that provides PCs with internet access and touch-sensitive screens to hotels
Suppose the Hard Rock Hotel and Casino in Las Vegas informs Uniguest that it is considering installing these systems in its hotel rooms. The Hard Rock expects to be able to charge higher prices for these rooms if it installs Uniguest's systems in its rooms. The two companies begin bargaining over what price the Hard Rock will pay Uniguest for its systems, and the decision tree shown above illustrates this bargaining game. Note that the profit figures listed in the decision tree are additional profits for the Hard Rock and total profits for Uniguest. a. Suppose the Hard Rock offers Uniguest $1,200 per system. Will Uniguest accept or reject this offer? Why? b. Suppose the Hard Rock offers Uniguest $800 per system. Will Uniguest accept or reject this offer? Why? c. Suppose Uniguest attempts to obtain a favorable outcome from the bargaining by telling the Hard Rock it will reject an $800-per-system offer. If the Hard Rock does not believe the threat is credible, what will it do? Why? What will Uniguest do? Why? d. Is there a subgame-perfect equilibrium in this situation? Explain.
Which of the following best explains what is happening when disposable income equals zero?
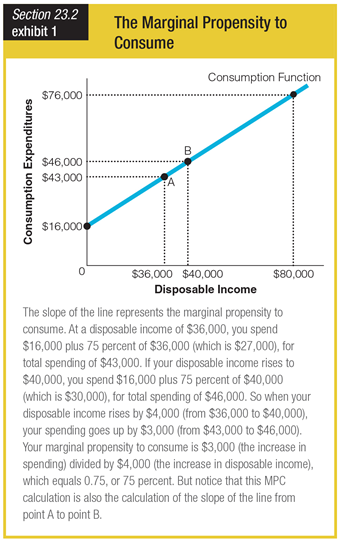
a. All consumption has ceased.
b. Income is positive but stagnant.
c. All money is being saved instead of spent.
d. Savings or credit is being used to pay for necessities.
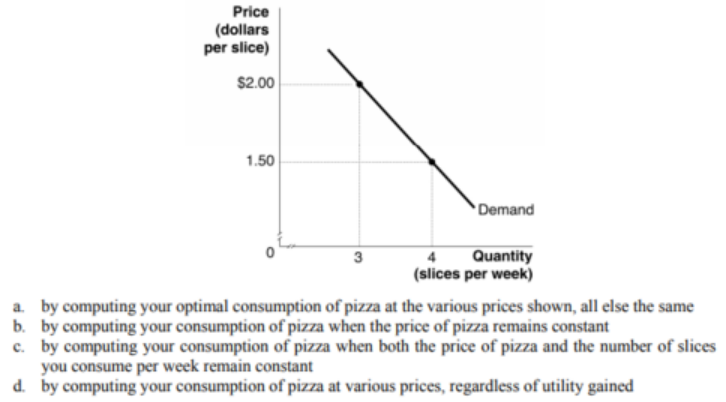
Refer to the graph below. The graph shows your weekly demand for pizza. How was this demand curve constructed?