One key purpose of economic regulation is
A. to force a firm to produce at the point at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue.
B. to control the quality of service provided by a monopolist.
C. to focus on the impact of production on the environment and society, the working conditions under which goods and services are produced, and sometimes the physical attributes of goods.
D. to control the price that regulated enterprises are allowed to charge.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
P-TV and QRS-TV are trying to decide whether to air a sitcom or a reality show in a given time slot. Viewers like both sitcoms and reality shows, but sitcoms are more expensive to produce than reality shows since real actors need to be hired. QRS-TV makes its decision first, and then P-TV observes that choice before making its decision. Both stations know all of the information in the decision tree below. 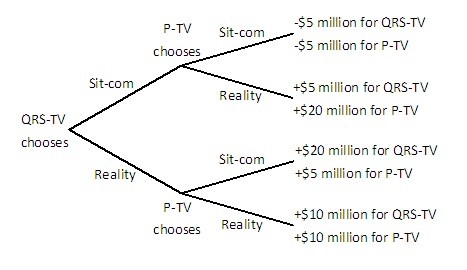 Given the information in this decision tree, if QRS-TV announces that it will air a reality show, it can expect to:
Given the information in this decision tree, if QRS-TV announces that it will air a reality show, it can expect to:
A. earn $10 million. B. lose $5 million. C. earn $20 million. D. earn $5 million.
Maude is complaining about how much she pays in taxes now that the economy is finally doing really well. Even though she's in the same tax bracket as she was last year, she's paying $500 more in taxes this year, just because she earned more overtime pay this year. Maude's increased tax payment to the government is an example of:
A. automatic stabilizers. B. discretionary fiscal policy. C. expansionary fiscal policy. D. contractionary fiscal policy.
Assume that five oligopolists begin with a common price of p = $15. One of the firms raises its price to $18. What are the other four firms likely to do, based on the theory of the kinked demand curve?
A. Raise their prices also, but by less than $3 B. Raise their prices by $3 C. Keep their prices the same D. Lower their prices by less than $3
The gap that exists when equilibrium real GDP is less than full-employment real GDP is
A. an inflationary gap. B. the short-run aggregate supply curve. C. a recessionary gap. D. money illusion.