An optimal tax is one that minimizes the
a. external benefit.
b. total deadweight loss from the tax.
c. income taxes.
d. horizontal equity.
b
You might also like to view...
The amount by which an aggregate expenditures schedule must shift upward to achieve the full-employment real GDP is a(n)
A. recessionary expenditure gap. B. negative net export gap. C. expenditure multiplier gap. D. inflationary expenditure gap.
If the supply of loanable funds shifts right, then
a. the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both fall. b. the real interest rate falls and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds rises. c. the real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds both rise. d. the real interest rate rises and the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds falls.
The figure below represents the U.S. market for steel imports from Korea. The Korean government provides an export subsidy of $25 per ton, and Korean firms use the subsidy to reduce their export price to the United States to $375 per ton.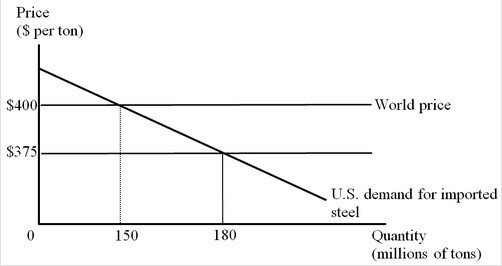 Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?
Suppose the United States now imposes a countervailing duty on the imports of steel at the rate of $25 per ton. Which of the following is true in this context?
A. Korea's loss of well-being exceeds the U.S. gain of well-being. B. The world price level and volume of trade become similar to the free-trade condition. C. The well-being of the world as a whole is reduced by $750 million. D. The producers in the United States lose, whereas the producers in Korea gain.
By restricting foreign lending, a country with sufficient market power can
A. increase world production. B. lower world interest rates. C. bid up the rate that foreign borrowers have to pay. D. bid up the rate that domestic lenders get after taxes.