Consider the following hypothetical scenarios:
Scenario A: You are about to purchase a pair of 7 for All Mankind jeans for $175 and a t-shirt for $45.
The sales attendant at the store tells you that the pair of jeans you wish to buy is on sale for $160 at another store, located about a 20-minute drive away.
Scenario B: You are about to purchase a pair of 7 for All Mankind jeans for $175 and a t-shirt for $45. The sales attendant at the store tells you that the t-shirt you wish to buy is on sale for $30 at another store, located about a 20-minute drive away.
Based on standard economic theory, under which scenario would you make the 20-minute trip to the other store?
A) Scenario A because the pair of jeans is a very expensive item and $15 saving is quite substantial
B) Scenario B because a $15 saving amounts to a substantial discount (about 33 percent)
C) in either scenario if I think a $15 savings is worth the 20-minute trip
D) in none of these scenarios if I think the $15 saving is not worth the 20-minute trip
E) C and D are correct answers.
E
You might also like to view...
P-TV and QRS-TV are trying to decide whether to air a sitcom or a reality show in a given time slot. Viewers like both sitcoms and reality shows, but sitcoms are more expensive to produce than reality shows since real actors need to be hired. QRS-TV makes its decision first, and then P-TV observes that choice before making its decision. Both stations know all of the information in the decision tree below. 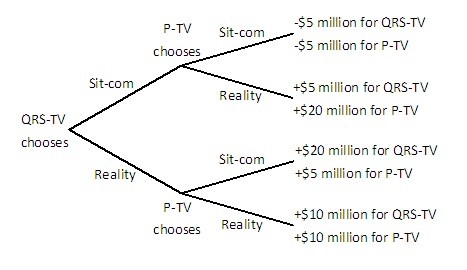 Given the information in this decision tree, if QRS-TV announces that it will air a reality show, it can expect to:
Given the information in this decision tree, if QRS-TV announces that it will air a reality show, it can expect to:
A. earn $10 million. B. lose $5 million. C. earn $20 million. D. earn $5 million.
The classic example used to discuss the problem of adverse selection is:
A. fruit and produce markets, such as lemons. B. workers who shirk when their effort isn’t closely monitored. C. the imbalance of information that exists between a buyer and seller of a used car. D. drivers with insurance who tend to drive more recklessly.
When a business advertises that its product has unique features that make it superior to other similar products, it is engaging in
A. Price competition. B. Product differentiation. C. Predatory pricing. D. Contestable market advertising.
If the population is growing faster the economy, then per-capita output is falling.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)