In the long run, a tax placed on a perfectly competitive industry should
A. increase the number of firms.
B. not affect the number of firms.
C. decrease the number of firms.
D. One cannot tell
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
According to OLI theory, a firm might be unwilling to license its production to a foreign firm for fear that its technology may be stolen or its brand name harmed, which leads the firm to internalize control over its asset and set up its own foreign
subsidiary. Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Policies aimed at reducing the natural rate of unemployment are referred to as
a. stabilization policies. b. structural policies. c. macroeconomic policies. d. labor policies.
If government undertakes to reduce water usage by using a market incentive plan:
A. consumers will be asked to reduce water usage voluntarily. B. consumers who reduce water usage by more than the required amount can sell marketable certificates to consumers who seek to reduce usage by less than the required amount. C. each consumer will have to reduce his or her water usage by an equal amount. D. consumers who do not reduce usage by the required amount will have to pay taxes on the extra water usage.
In this graph of a firm’s supply and demand for labor, at what point are profits of labor maximized?
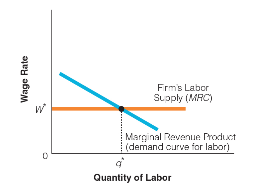
a. before MRP reaches W*
b before q* reaches W*
c. when there are q* workers
d. when quantity is highest