Suppose the required reserve ratio was 10% and then it increased to 20%. This would
a) result in a drop in the money multiplier from 10 to 5.
b) increase the amount of excess reserves available.
c) result in an increase in the money multiplier from 5 to 10.
d) have no impact on the money multiplier.
Ans: a) result in a drop in the money multiplier from 10 to 5.
You might also like to view...
Refer to the figure below. At the original market equilibrium: 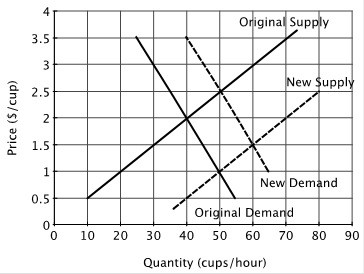
A. 40 cups are sold per hour at a price of $2.00 each. B. 50 cups are sold per hour at a price of $2.50 each. C. 50 cups are sold per hour at a price of $1.00 each. D. 60 cups are sold per hour at a price of $1.50 each.
The theory of purchasing power parity suggests that, in the long-run, exchange rates are determined by ________
A) relative interest rate levels B) relative price levels C) the GDP values for the two countries D) the most significant monetary authorities, including the Federal Reserve, European Central Bank, Bank of England and the Bank of Japan
For the typical consumer, present consumption is
a. preferred to future consumption b. not preferred to future consumption c. preferred to future saving d. not preferred to future saving e. financed out of present saving
Entry of new firms causes
A) accounting profits to go to zero. B) market share to grown. C) economic profits to go to zero. D) total revenue to be maximized.