The purchasing power parity theory is not a good explanation of how nominal exchange rates are determined in the short run because:
A. there is no evidence that low inflation is associated with less rapid nominal exchange rate depreciation.
B. most nominal exchange rates are fixed and foreign exchange markets do not bring the supply and demand for currencies into equilibrium.
C. many goods and services are not traded internationally and not all internationally-traded goods are standardized.
D. most goods and services are traded internationally and are standardized.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Evidence from the United States and Japan on "multifactor productivity" shows it to be highly ________, which is ________ with the RBC theory of technological shocks and their consequences for the business cycle
A) procyclical, consistent B) procyclical, inconsistent C) countercyclical, consistent D) countercyclical, inconsistent
What is the price elasticity of demand for a vertical demand curve?
a. Inelastic, but not perfectly inelastic b. Perfectly elastic c. Unitary elastic d. Perfectly inelastic e. Elastic, but not perfectly elastic
Which panel of Figure 3.3 represents the changes in the market for beef when the price of corn (cattle feed) rises and the people become more fearful of mad cow disease?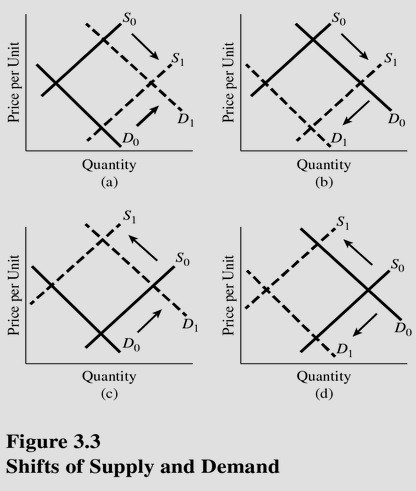
A. A. B. B. C. C. D. D.
The full-employment level of real GDP is the level which can be produced with:
A. given technology and productive resources. B. frictional and structural unemployment equal to zero. C. cyclical unemployment greater than zero. D. future technology.