Identify and briefly describe the function of the labeled structures in the human eye pictured here. 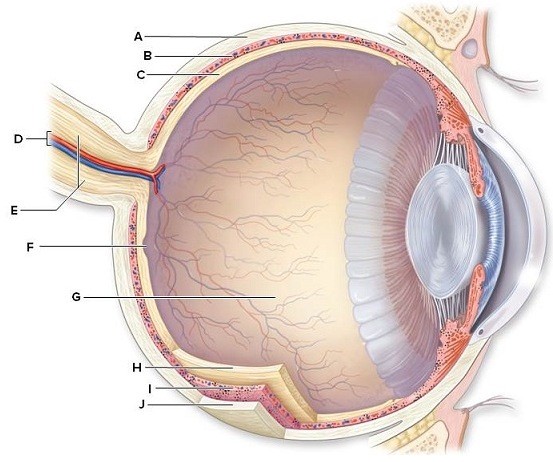 A:________B:________C:________D:________E:________F:________G:________H:________I:________J:________
A:________B:________C:________D:________E:________F:________G:________H:________I:________J:________
What will be an ideal response?
A: Sclera: protects and supports the eyeball
B: Choroids: absorbs stray light
C: Retina: contains sensory receptors for light
D: Retinal blood vessels: brings blood to and from the eye, providing oxygen and nutrients and removal of waste
E: Optic Nerve: transmits visual information from the retina to the brain
F: Fovea centralis: area of the retina where cone cells are densely packed; makes acute vision possible
G: Posterior compartment filled with vitreous humor: supports eyeball and transmits light
H: Retina: contains sensory receptors for light
I: Choroid: absorbs stray light
J: Sclera: protects and supports eyeball
You might also like to view...
The nucleolus is the site of:
A. protein synthesis. B. uncoiling and unraveling of chromosomes. C. ribosome assembly. D. lipid synthesis. E. chromosome replication.
What happens to a cell that is placed in an isotonic solution?
a. The cell swells. b. The cell shrinks. c. The cell stays the same size. d. The cell crenate.
A species that consumes both plant and animal tissue is called a(n) ________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
Chemical energy:
A) is a form of potential energy stored in bonds between molecules. B) contains less energy than kinetic energy. C) is kinetic energy that has not been converted to heat. D) is best described as "the energy of motion." E) is stored energy that is unavailable to do work.