How does inhibition of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction by a competitive inhibitor differ from inhibition by a noncompetitive inhibitor?
A) Competitive inhibitors interfere with the enzyme; noncompetitive inhibitors interfere with the reactants.
B) Competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme reversibly; noncompetitive inhibitors bind to it irreversibly.
C) Competitive inhibitors change the enzyme's tertiary structure; noncompetitive inhibitors cause polypeptide subunits to dissociate.
D) Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of the enzyme; noncompetitive inhibitors bind to a different site.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Genetic recombination as a result of crossing
over occurs more readily in genes
a. that are on the sex chromosomes. b. that are on the autosomes. c. that are located close together on the same chromosome. d. that are located far apart on the same chromosome. e. that are located on different chromosomes.
In a marine environment, what is the function of the structure on Figure 48-2 labeled A?
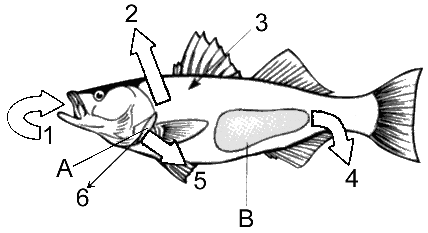
a. salt excretion
b. water gain by osmosis
c. drinking
d. removal of salts and nitrogenous wastes from the blood
e. release of nitrogenous wastes
Which of the following statements would not be consistent with the theory for the endosymbiotic origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
A. Genes encoded within mitochondria and chloroplasts indicate a closer relationship to prokaryotes than do most nuclear genes. B. The composition of the outer membrane of chloroplasts and mitochondria is similar to the plasma membrane of eukaryotic cells. C. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have some enzymes unique to them. D. Mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA enclosed within a nuclear envelope. E. The composition of the inner membrane of chloroplasts and mitochondria is similar to the plasma membrane of prokaryotic cells.
The ________ are fungi that lack mitochondria, peroxisomes, and centrioles.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).