Refer to the information provided in Figure 5.6 below to answer the question that follows.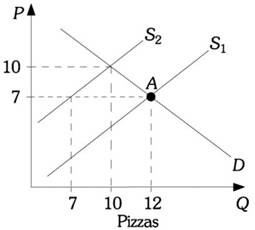 Figure 5.6Refer to Figure 5.6. The market is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve S2. If supply shifts from S2 to S1, which of the following statements is true?
Figure 5.6Refer to Figure 5.6. The market is initially in equilibrium at the intersection of the demand curve and supply curve S2. If supply shifts from S2 to S1, which of the following statements is true?
A. The market cannot move to a new equilibrium unless demand shifts at the same time that supply shifts.
B. There is no need for price to serve as a rationing device in this case because the new equilibrium quantity is less than the original equilibrium quantity.
C. Price will still serve as a rationing device causing quantity demanded to rise from 10 to 12 pizzas.
D. Price will still serve as a rationing device causing quantity supplied to exceed 12 pizzas.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
For a monopsonist, marginal factor cost exceeds the wage rate since
A) more workers have to be paid the prevailing wage rate. B) the supply of labor is perfectly elastic. C) when new workers are hired the wage rate must be increased for all workers and not just for the additional workers. D) the labor demand is downward sloping.
The Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) is an example of
A. a price leadership system. B. a generally unsuccessful cartel. C. an organization devoted to tacit collusion. D. a successful cartel.
If people never withdraw cash from banks and there are no required reserves, how much money can the banking system potentially create for a given amount of new deposits?
A. None. B. The same amount as the new deposits. C. An infinite amount of money. D. The amount of new deposits multiplied by the reserve ratio.
Refer to the diagram of the market for money. Given D m and S m , an interest rate of i 3 is not sustainable because the:
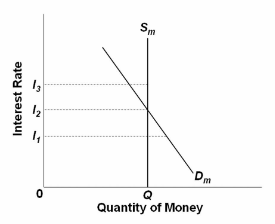
A. supply of bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise.
B. supply of bonds in the bond market will increase and the interest rate will decline.
C. demand for bonds in the bond market will decline and the interest rate will rise.
D. demand for bonds in the bond market will rise and the interest rate will fall.