Resolving Adam Smith's diamond-water puzzle involves
a. realizing that price is not directly related to total utility.
b. knowing that at optimal purchase, price will tend to equal marginal utility.
c. knowing that, as increasing quantities of a good are consumed, marginal utility diminishes and, conversely, consuming a small quantity of a good produces high marginal utility.
d. All of the above are correct.
d
You might also like to view...
Use the figure below to answer the following question. 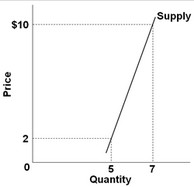 Assume that price increases from $2 to $10. The price elasticity of supply (based on the midpoint formula) associated with this price change is about
Assume that price increases from $2 to $10. The price elasticity of supply (based on the midpoint formula) associated with this price change is about
A. 0.25 and supply is inelastic. B. 1 and supply is unit-elastic. C. 1.35 and supply is elastic. D. 4 and supply is elastic.
The magnitude of the slope of the budget line measures the
A) opportunity cost of the good on the horizontal axis in terms of the good on the vertical axis. B) opportunity cost of the good on the vertical axis in terms of the good on the horizontal axis. C) price elasticity of demand. D) price elasticity of supply.
Consider the market for nurses in a given city. In each of the following cases, explain what happens to the equilibrium wage rate and the quantity of nurses hired
a. One of the major hospitals in the city closes. b. A record number of students graduate with bachelor's degrees in nursing. c. Traditionally, nursing is a field that attracts women. However, changes in access to education and to the labor force participation rate by women have led to a greater demand for the services of women in a wide range of occupations. The demand for nurses, however, does not change. d. Advances in medical technology reduce the amount of time physicians must spend with patients in intensive care and increase the time that nurses spend with patients.
All of the following can cause conflict between divisions EXCEPT
a. Divisional managers are rewarded on the profitability of the firm, instead of profitability of the division b. managers of profit centers care too little about the effects of their decisions on other divisions c. managers are rewarded only for how much profit their division generates d. corporate executives cannot tell when one divisional manager's decisions are appropriate or not