Light from an astronomical source is found to be shifted to a one percent lower frequency than had the source been at rest. What radial velocity could cause such a shift?
A. 
m/s moving away from the observer
B. 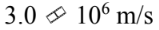
m/s moving away from the observer
C. 
m/s moving toward the observer
D. 
m/s moving toward the observer
E. 
m/s moving away from the observer
B. 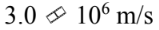
m/s moving away from the observer
You might also like to view...
Fluid Flow: Consider a very small hole in the bottom of a tank that is 17.0 cm in diameter and filled with water to a height of 90.0 cm. Find the speed at which the water exits the tank through the hole.
A. 4.20 m/s B. 17.64 m/s C. 44.1 m/s D. 48.3 m/s
The position of an object that is oscillating on an ideal spring is given by the equation x = (12.3 cm) cos[(1.26s-1)t]. At time t = 0.815 s,
(a) how fast is the object moving? (b) what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the object? What will be an ideal response?
You find yourself in a place that is unimaginably hot and dense. A rapidly changing gravitational field randomly warps space and time. Gripped by these huge fluctuations, you notice that there is but a single, unified force governing the universe
Where are you? A) You are floating somewhere in the universe near its end, 10100 years from now. B) You are in the center of a young star. C) You are in the universe shortly after inflation. D) You are inside the nucleus of an atom. E) You are in the early universe before the Planck time.
A solid steel ball is dropped from a great height and when its speed reaches 20 m/s its acceleration downward is 7.35 m/s2 . What would be the terminal velocity in this situation?
a. 80 m/s c. 40 m/s b. 60 m/s d. 20 m/s