Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.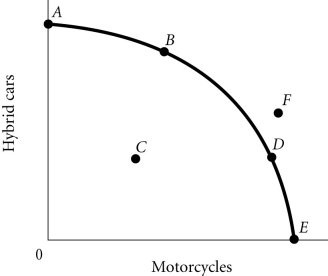 Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
Figure 2.4According to Figure 2.4, as the economy moves from Point D to Point B, the opportunity cost of hybrid cars, measured in terms of motorcycles,
A. decreases.
B. remains constant.
C. increases.
D. initially increases, then decreases.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is an example of consumer surplus?
A) Jose buys a hamburger for $2 and tells you he would not have paid a penny more. B) John believes the price he paid for his computer was too high. C) Mary buys a paper tablet for $2 and finds the same good at another store for $1.50. D) Sue would have paid $15 for a new compact disc but paid only $10. E) Anne finds a mountain bike for which she is willing to pay a maximum of $550 and the price of the bike is $600.
The most likely reason why Los Angeles has so much smog is that residents
a. do not have strong, enforceable property rights to rapid transit b. do not have strong, enforceable property rights to clean air c. prefer dirty air to the inconvenience of rapid transit d. prefer dirty air to the inconvenience of carpools e. prefer dirty air to the inconvenience of eliminating smog
Suppose there is only one producer of frames, a necessary component in manufacturing computer monitors. Because of the threat of entry, this firm charges its customers a price equal to average cost. One reason that a producer of computer monitors may make rather than buy frames is
a. the frame supplier may be unreliable b. the total cost of the components of frames is the same as the price of frames purchased in the market c. the frame manufacturer has no incentive to make high-quality frames d. managers at the computer monitor firm place a high value on their time e. the frame manufacturer will soon go out of business because firms do not produce goods for the market that can be made in-house
A change in quantity demanded of a good always results from a change in
a. income b. tastes c. the price of the good d. both income and tastes e. the price of other goods