Try using a stopwatch to time the execution of the programs in this chapter. Time from hitting return on the command until the next prompt appears. What is the relationship between execution time and the length of the sound? Is it a linear relationship (i.e., longer sounds take longer to process and shorter sounds take less time to process)? Or is it something else? Compare the individual programs. Does normalizing a sound take longer than raising (or lowering) the amplitude a constant amount? How much longer? Does it matter whether the sound is longer or shorter?
What will be an ideal response?
The precise amount of time will depend on the computer’s processing power on which the algorithms are run on. However, in general longer sounds run on the same function take longer. Functions that involve iterating more also take longer. This means that normalizing takes the longest out of the programs in this chapter as it involves iterating over the entire length of the sound twice.
You might also like to view...
You have been tasked with training end users in security best practices and have observed a trend among users in which many are writing down their passwords. Which of the following procedures can be implemented to provide enough security to protect resources while minimizing the need for users to write down their passwords?
A. Disable password complexity requirement. B. Disable required passwords. C. Lengthen the time period between forced password changes. D. Increase password length requirement.
Why did a normal CRT monitor have three electron guns?
What will be an ideal response?
When an organization wants to use encryption, it requests a set of associated public and private keys from a ____.
A. proxy server B. network administrator C. network firewall D. certification authority
Use the results in part (a) to compute the confidence for the association rules {b, d} ?? {e} and {e} ?? {b, d}. Is confidence a symmetric measure?
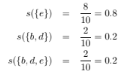
Consider the data set shown in Table 6.1.