Refer to Figure 15-1. The use of antibiotic medium at the end of this process:
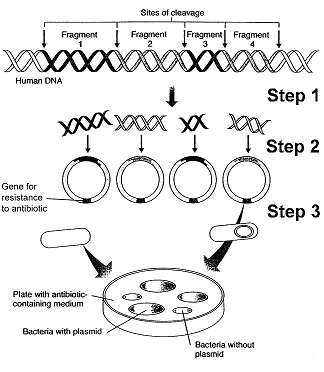
a. selects against plasmids containing human DNA fragments.
b. selects for plasmids containing particular DNA fragments.
c. selects for bacteria containing plasmids.
d. selects for bacteria lacking plasmids.
e. prevents contamination of the medium
C
You might also like to view...
The general name for enzymes that catalyze RNA synthesis directed by a DNA template is:
A. RNA synthetase. B. RNA polymerase. C. polynucleotide phosphorylase. D. RNase. E. DNA polymerase.
A pro- strain of bacteria, which has not been in contact with any other strains, develops the ability to produce the amino acid proline. This mutant "rescue" could have been caused by
A. addition of the pro+ gene via transduction. B. mutation of the pro- gene during phage integration. C. removal of the pro- gene during excision. D. addition of the pro+ gene via transformation. E. correction of the pro- gene by reverse transcriptase.
Which of the following is a plant behavior that is influenced by light?
A. solar tracking B. phototropism C. flowering D. seed germination E. All of the choices are true
The structural difference between saturated and unsaturated fats causes what type of change at room temperature?
A. Linear structure of a fatty acid causes solid formation at room temperature. B. Double bonds in saturated fatty acids cause a solid structure at room temperature. C. A linear structure causes a loose forming macromolecule that is liquid at room temperature. D. The double bonds require higher temperatures at room temperature to make this fatty acid into a liquid.