An 8.0-kg object moving 4.0 m/s in the positive x direction has a one-dimensional collision with a 2.0-kg object moving 3.0 m/s in the opposite direction. The final velocity of the 8.0-kg object is 2.0 m/s in the positive x direction. What is the total kinetic energy of the two-mass system after the collision?
a. 32 J
b. 52 J
c. 41 J
d. 25 J
e. 29 J
c
You might also like to view...
In the light curve below, what is the period of the eclipsing binary?
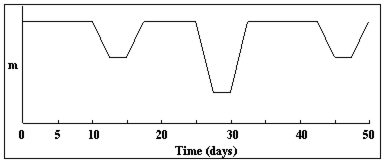
a. 5 days
b. 32.5 days
c. 7.5 days
d. 42.5 days
e. 50 days
According to the nebular theory of solar system formation, which of the following best explains why the solar nebula ended up with a disk shape as it collapsed?
A) As the nebula shrank and rotated faster, collisions between orbiting particles caused it to flatten into a disk. B) The nebula was fairly flat to begin with, and retained this flat shape as it collapsed. C) The force of gravity pulled material that was spherically distributed downward into a flat disk. D) the law of conservation of energy
The number of protons in a neutral atom is balanced by an equal number of
A) electron shells that surround the nucleus. B) neutrons in the nucleus. C) orbital electrons. D) none of the above
Identify (name) the 12 leptons:
What will be an ideal response?