What would happen if a transformer had the same number of loops on each side?
What will be an ideal response?
The input and output potential differences (voltages) would be the same. So
would the input and output currents.
You might also like to view...
When the standing wave pattern in a pipe is NANA, the pipe has which of the following set of properties? (N stands for node, A for antinode.)
a. It is open at both ends. b. It is closed at both ends. c. It is open at one end and closed at the other end. d. Any of the above could be true.
Diffraction takes place:
a. on highly reflective surfaces. b. on rough surfaces. c. around the edges of barriers. d. for waves moving through empty space. e. in the center of shadows.
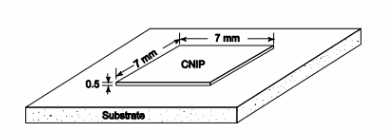
A square silicone chip 7 mm by 7 mm in size and 0.5 mm thick is mounted on a plastic substrate as shown in the sketch below. The top surface of the chip is cooled by a synthetic liquid flowing over it. Electronic circuits on the bottom of the chip generate heat at a rate of 5 watts that must be transferred through the chip. Estimate the steady state temperature difference between the front and back surfaces of the chip. The thermal conductivity of silicone is 150 W/(m K).
GIVEN
A 0.007 m by 0.007 m silicone chip
Thickness of the chip (L) = 0.5 mm = 0.0005 m
Heat generated at the back of the chip (Gq) = 5 W
The thermal conductivity of silicon (k) = 150 W/(m K)
FIND
The steady state temperature difference (?T)
ASSUMPTIONS
One dimensional conduction (edge effects are negligible)
The thermal conductivity is constant
The heat lost through the plastic substrate is negligible
SKETCH
A thrown stone hits a window but doesn't break it. Instead, it reverses direction and ends up on the ground below the window. In this case, we know:
a. the force of the stone on the glass > the force of the glass on the stone. b. the force of the stone on the glass = the force of the glass on the stone. c. the force of the stone on the glass < the force of the glass on the stone. d. the stone didn't slow down as it hit the glass.