The heat conduction equation in cylindrical coordinates is
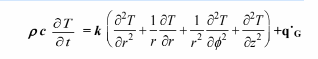
(a) Simplify this equation by eliminating terms equal to zero for the case of steady-state heat flow
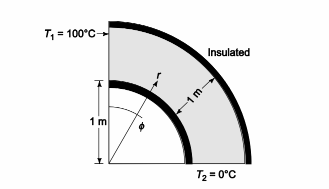
without sources or sinks around a right-angle corner such as the one in the accompanying
sketch. It may be assumed that the corner extends to infinity in the direction perpendicular to
the page. (b) Solve the resulting equation for the temperature distribution by substituting the
boundary condition. (c) Determine the rate of heat flow from T1 to T2. Assume k = 1 W/(m K)
and unit depth .
GIVEN
• Steady state conditions
• Right-angle corner as shown below
• No sources or sinks
• Thermal conductivity (k) = 1 W/(m K)
FIND
(a) Simplified heat conduction equation (b) Solution for the temperature distribution (c) Rate of heat flow from T1 to T2 ASSUMPTIONS
• Corner extends to infinity perpendicular to the paper
• No heat transfer in the z direction
• Heat transfer through the insulation is negligible
SKETCH
The boundaries of the region are given by
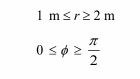
Assuming there is no heat transfer through the insulation, the boundary condition is
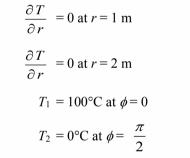
(a) The conduction equation is simplified by the following
Steady state
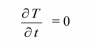
No sources or sinks
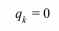
No heat transfer in the z direction

Substituting these simplifications into the conduction equation
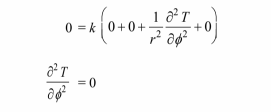
(b) Integrating twice
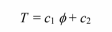
The boundary condition can be used to evaluate the constants
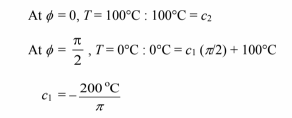
Therefore, the temperature distribution is
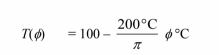
(c) Consider a slice of the corner as follow
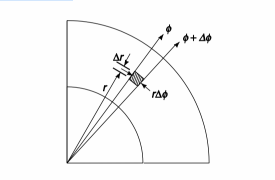
The heat transfer flux through the shaded element in the ? direction is
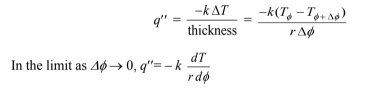
Multiplying by the surface area drdz and integrating along the radius
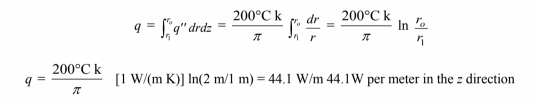
You might also like to view...
A blackbody is an ideal system that
A) absorbs 100% of the light incident upon it, but cannot emit light of its own (i.e., a "black" body). B) emits 100% of the light it generates, but cannot absorb radiation of its own. C) either absorbs 100% of the light incident upon it, or emits 100% of the radiation it generates. D) absorbs 50% of the light incident upon it, and emits 50% of the radiation it generates.
If you stand in front of a concave mirror, exactly at its center of curvature,
A) you will see your image and you will appear smaller. B) you will see your image and you will appear larger. C) you won't see your image because there is none. D) you won't see your image because it's focused at a different distance. E) you will see your image at your same height; however it will be inverted.
Three capacitors have capacitances C1 < C2 < C3 . If these capacitors are connected in series, which of the following is true for the resulting equivalent capacitance?
a. Ceq < C1 b. Ceq > C3 c. Ceq = (C1 + C2 + C3)/3 d. None of the above is always correct.
Which of the following observations would not be likely to provide information about the final, explosive stages of a star's life?
A) studying the light rings around Supernova 1987A in the Large Magellanic Cloud B) decades of continuous monitoring of red giants in a globular cluster C) observing the structures of planetary nebulae D) neutrino detections from nearby supernovae