Suppose the intersection of the IS and LM curves is to the left of the FE line. What would most likely eliminate a disequilibrium among the asset, labor, and goods markets?
A. A rise in the price level, shifting the IS curve up and to the right
B. A fall in the price level, shifting the LM curve down and to the right
C. A fall in the price level, shifting the IS curve down and to the left
D. A rise in the price level, shifting the LM curve up and to the left
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The loss in social surplus that occurs when the economy produces at an inefficient quantity is called
a. efficiency. b. consumer surplus. c. social surplus. d. deadweight loss.
The chained consumer price index
a. assumes that households purchase the same bundle of goods and services over a lengthy time period. b. adjusts the quantities of the typical bundle purchased each month to reflect the substitution away from goods that have become more expensive. c. reflects changes in the prices of all final goods and services produced domestically by the citizens of a nation during a period. d. will generally result in a higher measured rate of inflation than the regular consumer price index.
Which of the following is an important advantage of discretionary monetary policy?
a. Influencing the political business cycle b. Flexibility to deal with changing economic conditions c. Limiting the opportunities for abuse of power by policymakers d. Avoiding the time inconsistency of policy problem
Refer to the diagram, where variable inputs of labor are being added to a constant amount of property resources. The total output of this firm will cease to expand:
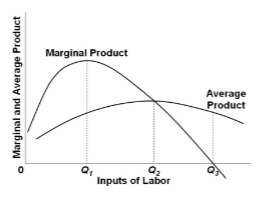
A. if a labor force in excess of Q 1 is employed.
B. if a labor force in excess of Q 2 is employed.
C. if a labor force in excess of Q 3 is employed.
D. only if the marginal product curve becomes negative at all levels of output.