The current account surplus is
A) an increasing function of disposable income and an increasing function of the real exchange rate.
B) a decreasing function of disposable income and a decreasing function of the real exchange rate.
C) a decreasing function of disposable income and an increasing function of the real exchange rate.
D) only a decreasing function of disposable income.
E) only an increasing function of the real exchange rate.
C
You might also like to view...
The perfectly competitive firm's supply curve is that portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the firm's average total cost curve
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
In Exhibit 1, what is the consumer surplus depicted when the quantity is three units?
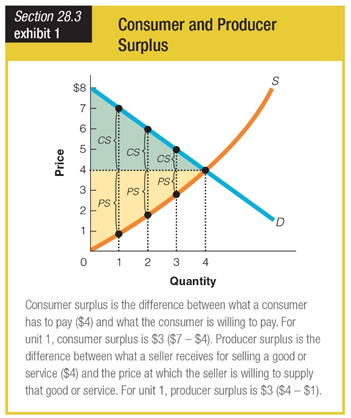
a. $4
b. $2
c. $1
d. $0
A monopolistically competitive firm differs from a perfectly competitive firm in the long run in that
A. profits are positive for a monopolistically competitive firm and zero for a perfectly competitive firm. B. the demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is downward sloping, while the demand curve faced by a perfectly competitive firm is horizontal. C. marginal cost equals the market price for a monopolistically competitive firm but not for a perfectly competitive firm. D. profits are zero for a monopolistically competitive firm and positive for a perfectly competitive firm.
If a natural monopoly was broken into several smaller competing firms,
A. Producers would be better off because they would have greater market share. B. Consumers would lose because of less competition. C. Workers would be worse off because fewer jobs would be available. D. Society would be worse off because the economies of scale would be destroyed.