The periodic law states that the properties of elements are periodic functions of their atomic
a. radii.
b. shells.
c. numbers.
d. masses.
c
You might also like to view...
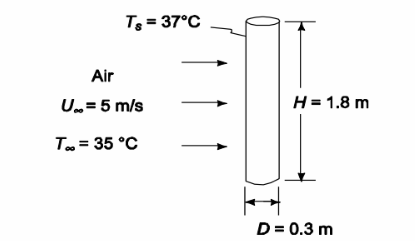
The human body is typically modelled as a vertical cylinder that is 1.8 m high and is 30 cm in diameter, as shown in the figure. Calculate the average rate of heat loss from this body, which is maintained at 37°C, on a windy day when the airstream has a 5 m/s velocity and is at 35°C. To ascertain “wind chill” effects, compare this result with the heat loss that would occur in “stagnant” conditions, or when it is not windy and the heat transfer is only by natural convection (consider an average heat transfer coefficient of 3.6 W/(m2 K) for free convection). What is the wind chill effect if the wind got stronger (10 m/s) and colder (25°C)? Even though the natural convection heat transfer coefficient also changes somewhat (as discussed later in Chapter 8), for this calculation
consider it to remain the same. Moreover, compare the heat loss in both cases with the typical energy intake, or metabolic heat production from consumption of food, of about 1033 kcal/day and comment upon your results.
GIVEN
• Human body modeled as a cylinder in an air stream
• Body surface temperature (Ts) = 37°C
• Air velocity (V?) = 5 m/s
• Air temperature (T?) = 35°C
• Cylinder diameter (D) = 30 cm = 0.3 m
• Cylinder height (H) = 1.8 m
FIND (a) The heat loss from the idealized human body
(b) Heat loss if the wind speed is 10 m/s and its temperature is 250C. (c) Compare with the free convection results of Problem 5.8 and with the typical food
consumption rate of 1033 kcal/day
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air velocity is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder
• Air flow approaching cylinder is laminar
• Heat transfer from the ends can be neglected
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0262 W/(m K) Kinematic viscosity (?) = 17.1 × 10–6 m2/s Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71 At the surface temperature of 37°C Prs = 0.71
A sound with ten times the amplitude of another sound is judged to be ten times as loud
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
What gives the Moon a coppery glow during a total eclipse?
a. Sunlight refracted through Earth's atmosphere b. Sunlight reflected from Earth's surface c. Not all of the sunlight is blocked out d. The artificial light reflected up from Earth's surface e. The spectral emissions of the gases that make up Earth's atmosphere.
A small railroad car is pulled by a rope as shown in the sketch (top view). The force F that the rope exerts on the car has a component along the track and another component perpendicular to the track
Judging from the diagram, the larger of these two components would be 1) along the track. 2) perpendicular to the track. These components will be equal if 3) the rope makes an angle of 45° with the track. 4) the rope is pulled in a direction along the track, rather than at an angle to it. 5) they form an action-reaction pair on the car. 6) but they can never really be equal.