When a market is not in equilibrium:
A. a change in either supply or demand is required to reestablish equilibrium.
B. the economic motives of sellers and buyers will move the market to its equilibrium.
C. government intervention is required to achieve equilibrium.
D. there is neither excess supply nor excess demand.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Which of the following leads to the suppliers paying all of a tax?
A) The supply is perfectly elastic. B) The supply is perfectly inelastic. C) The demand is unit elastic. D) The demand is perfectly inelastic.
Jess owns a sandwich shop. the price of a sandwich recently increased from $5 to $7. jess responded by increasing the quantity of sandwiches she supplied from 70 to 90 per day. using the midpoint method, jess's price elasticity of supply is equal to
a. 4 00. b. 0.75. c. 1.33. d. 3.00. e. 1.50.
Suppose the separation rate is 3% and the finding rate is 24%
a. What is the natural rate of unemployment? b. If the separation rate remains at 3% and finding rate doubles, what is the new natural rate of unemployment? c. If the separation rate is cut in half and the finding rate remains at 24%, what is the new natural rate of unemployment? d. Which has more impact: a doubling of the finding rate or a halving of the separation rate?
Refer to the information provided in Figure 7.10 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 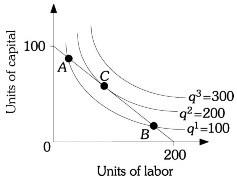 Figure 7.10Refer to Figure 7.10. If this firm's cost of capital is $10 per unit and its cost of labor is $5 per unit, the isocost line represents a total cost of
Figure 7.10Refer to Figure 7.10. If this firm's cost of capital is $10 per unit and its cost of labor is $5 per unit, the isocost line represents a total cost of
A. $1,000. B. $2,000. C. $3,000. D. $4,000.