During reabsorption, sodium ions cross the proximal tubule walls into the interstitial fluid principally
by means of
a. bulk flow.
b. active transport.
c. countercurrent multiplication.
d. phagocytosis.
e. endocytosis.
B
You might also like to view...
In eukaryotic cells, glycolysis occurs in:
A. the cytoplasm. B. the nucleus. C. the matrix of the mitochondria. D. the endoplasmic reticulum. E. vacuoles.
What is the function of tropomyosin in muscle cells?
A. Tropomyosin binds to actin molecules and brings about shortening of the muscles. B. Tropomyosin covers the myosin binding sites on the actin molecules, preventing contraction from occurring. C. Tropomyosin is the contractile unit of the muscle cell. D. Tropomyosin stores calcium.
Carbon dioxide generally enters the plant through pores called
A) mesophyll. B) stomata. C) the cuticle. D) connexons. E) bacteriochlorophylls
GGG and GGC are codons for the amino acid, glycine. A mutation caused the insertion of a cytosine in place of the guanine during DNA replication. Over many generations the DNA changes so that the frequency of GGC is similar to that of GGG. What is this phenomenon called? 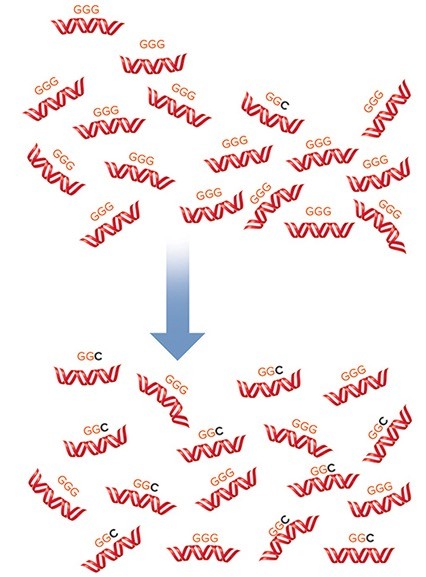
A. directional selection B. stabilizing selection C. neutral variation D. adaptive variation E. bottleneck effect