If a firm has a monopoly over the sale of camera drones and seeks to maximize profits, it:
A. adjusts the price of the product until demand becomes perfectly inelastic.
B. will set the price of the product so that its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost.
C. will set the price of the product equal to the marginal cost of production.
D. will set the price of the product equal to the average total cost of production.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
Tom spends all his income on comics and cola and maximizes his total utility. If the price of a comic is $4 and the price of a can of cola is $1, then the ratio of the ________ is 4
A) marginal utility from cola to the marginal utility from comics B) marginal utility from comics to the marginal utility from cola C) number of comics Tom buys to the number of cola Tom buys D) total utility from comics to the total utility from cola
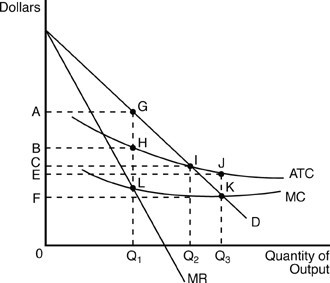 In the above figure, the area of rectangle ABHG represents the monopolist's
In the above figure, the area of rectangle ABHG represents the monopolist's
A. average total profits. B. maximized economic profits. C. total costs. D. maximized total revenue.
As you move down the production possibility frontier, the absolute value of the marginal rate of transformation
A. increases. B. initially decreases, then increases. C. decreases. D. initially increases, then decreases.
The Lucas supply function, in combination with the assumption that expectations are rational, implies that
A. both anticipated monetary and fiscal policy changes will affect real output. B. neither anticipated monetary policy changes nor anticipated fiscal policy changes will have an effect on real output. C. an anticipated monetary policy change will have no effect on real output, but an anticipated fiscal policy change will have an effect on real output. D. an anticipated monetary policy change will have an effect on real output, but an anticipated fiscal policy change will not have an effect on real output.