Identify the form of the integral as inverse sine, inverse tangent, logarithmic, or general power.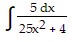
A. Inverse tangent
B. General power
C. Inverse sine
D. Logarithmic
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Find all the second order partial derivatives of the given function.f(x, y) = x2 + y - ex+y
A. fxx(x, y) = 2 - ex+y; fyy(x, y) = - ex+y; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = -ex+y B. fxx(x, y) = 2 + ex+y; fyy(x, y) = ex+y; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = ex+y C. fxx(x, y) = 2 - y2ex+y; fyy(x, y) = -x2ex+y; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = - y2ex+y D. fxx(x, y) = 1 - ex+y; fyy(x, y) = - ex+y; fyx(x, y) = fxy(x, y) = -ex+y
Use the given transformation to evaluate the integral. src="https://sciemce.com/media/4/ppg__tttt0613191206__f1q31g7.jpg" alt="" style="vertical-align: -4.0px;" />
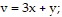
 Rwhere R is the parallelogram bounded by the lines
Rwhere R is the parallelogram bounded by the lines 


A. 2464
B. 1232
C. 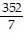
D. 
Identify the equation as linear or nonlinear.4x + 2y = -4
A. linear B. nonlinear
If a triangle has vertices of 
 and
and  then the area of the triangle is given by
then the area of the triangle is given by 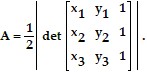 Find the area of the triangle with vertices at the given points.(1, -3) (1, 1) (4, 3)
Find the area of the triangle with vertices at the given points.(1, -3) (1, 1) (4, 3)
A. 6 B. 2.5 C. 12 D. 5