"Although the price levels appear to display short-run stickiness in many countries, a change in the money supply creates immediate demand and cost pressures that eventually lead to future increase in the price level." Discuss
What will be an ideal response?
(See Section 7). The statement is true. The pressures come from three main sources: excess demand for output and labor; inflationary expectations; and, raw material prices.
You might also like to view...
On an average, growth in per capita income is associated with a:
A) fall in inequality. B) fall in poverty. C) rise in poverty. D) rise in inequality.
Suppose the economy is producing above potential GDP and the Federal Reserve implements the appropriate change in monetary policy, but not until after the economy has started to slow down on its own. In this situation there is a real danger that
A) the Fed's expansionary policy will result in too small of an increase in GDP. B) the Fed's expansionary policy will result in too large of an increase in GDP. C) the Fed's contractionary policy will result in too large of a decrease in GDP. D) the Fed's contractionary policy will result in too small of a decrease in GDP.
What does the term "commitment" refer to in game theory?
What will be an ideal response?
Exhibit 7-12 Marginal revenue and cost per unit curves
?
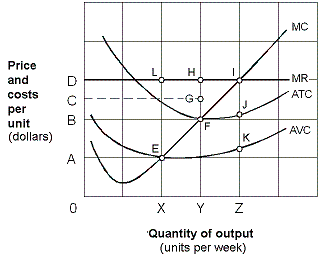
A. zero units of output because it is unprofitable. B. X units and incur a loss. C. Y units and break even. D. Z units and make an economic profit.