Consider the utility function 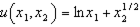 . (Explain all your answers.)
. (Explain all your answers.)
a. Derive the function for the marginal rate of substitution.
b. Do the tastes represented by this utility function satisfy diminishing MRS?
c. The marginal utility of a good is defined as the change in utility from additional consumption of that good (holding all else constant). Derive the marginal utility of 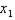
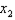
d. Why does an ordinal approach to utility theory not any attention to what you derived in (c)?
e. Why does an ordinal approach to utility not treat the marginal rate of substitution the way it treats the marginal utility concept?
What will be an ideal response?
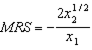
b. Holding
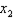 fixed, our MRS function decreases (in absolute value) as
fixed, our MRS function decreases (in absolute value) as 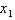 increases --- i.e. the slope of the indifference curves becomes shallower as we move to the right. Thus, the tastes indeed satisfy diminishing MRS.
increases --- i.e. the slope of the indifference curves becomes shallower as we move to the right. Thus, the tastes indeed satisfy diminishing MRS.c.
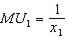 and
and 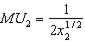
d. The marginal utility of a good is in "utility units" --- it gives us the additional utility the individual gets from more consumption of one of the goods. An ordinal approach to utility assumes utility cannot be measured objectively --- and therefore utility-denominated concepts lack solid interpretation.
e. The marginal rate of substitution is not in utility units --- but rather in units of
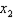 that are objectively measurable. The reason for that is that the MRS is composed of one MU divided by another -- which cancels the utility units; i.e.
that are objectively measurable. The reason for that is that the MRS is composed of one MU divided by another -- which cancels the utility units; i.e.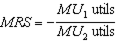
You might also like to view...
As the amount of inventories maintained by a firm increases:
A) its elasticity of supply increases. B) its elasticity of supply decreases. C) the elasticity of demand for its product increases. D) the elasticity of demand for its product decreases.
A union representing a group of workers will tend to be stronger when
a. there are no good substitutes for the labor services of the unionized workers. b. the domestic producers of the good produced by the unionized workers face intense competition from foreign suppliers of the good. c. the cost of employing the unionized workers is a large part of the total cost of the product that they produce. d. the demand for the good produced by the unionized workers is highly elastic.
If the government institutes an investment tax credit and decreases income taxes,
a) real GDP falls, and the price level could rise, fall, or stay the same. b) real GDP and the price level fall. c) real GDP rises, and the price level could rise, fall, or stay the same. d) real GDP and the price level rise.
A negative demand shock could cause an increase in U.S. exports.
Answer the following statement true (T) or false (F)