If a market basket was defined in 2014 and it cost $10,000 to purchase the items in that basket in 2014, while it cost $11,000 to purchase those identical goods in 2015, then the inflation rate from 2013 to 2014 is
A. (100-90.9)/100*100%=9.1%.
B. (110-100)/100*100%=10%.
C. (100-100)/100*100%=0%.
D. unknown given this data.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Currently the Fed targets
A) the inflation rate B) the exchange rate. C) the federal funds rate. D) both the monetary base and the federal funds rate simultaneously. E) the price level.
Answer the following statements true (T) or false (F)
1) Effective managers use marginal analysis to determine how much to spend on actions to lower the probability of bad outcomes.
2) The expected marginal benefit of reducing the probability of an accident is equal to the decrease in the expected cost of the accident.
3) 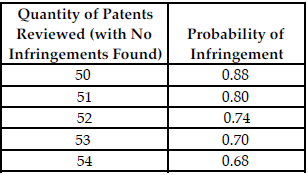
The above table shows the quantity of patents reviewed by a firm's attorney and the corresponding probability that the firm will infringe on another firm's patent. The cost of infringement is $50,000.
The expected marginal benefit of reviewing additional patents increases as the number of patents reviewed increases.
4) If actions to reduce the expected cost of an accident are equally effective, managers should authorize the most expensive actions first.
5) It is not optimal to drive the probability of a patent infringement to zero.
6) In some situations, managers cannot make incremental actions to prevent product failure and must either decide to take preventative action or not.
Non-inflation-adjusted ("nominal") gasoline prices reached their all-time highs in
A. 2001. B. 2008. C. 1991. D. 1982.
U.S. securities firms recently agreed to pay a record amount of $1.4 billion in settlement charges brought by government regulators. Regulators claimed that firms had abused investors during the market boom of the 1990s. Abuses included analysts
tailoring their research reports and ratings on the stocks they covered in order to win more business for their firm. If this settlement causes Wall Street firms to comply with the letter of the law but they violate the spirit of the law, the firms are engaging in A) elimination of conflicts of interest. B) creative response. C) the capture hypothesis. D) deregulation.