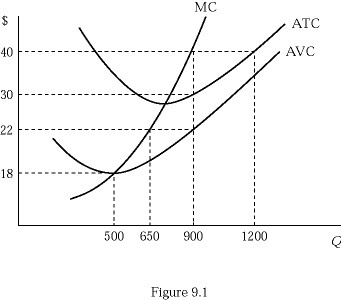
 Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
Figure 9.1 shows the cost structure of a firm in a perfectly competitive market. If the market price is $40 and the firm is currently producing the profit maximizing output level, its total variable cost is:
A. $12,500.
B. $14,300.
C. $19,800.
D. $27,000.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Based on the table above which shows Chip's costs, if Chip shuts down in the short run, his total cost will be
A) $0. B) $1,000. C) $1,200. D) $4,000.
Table 7-4 ? 6 346 490 600 692 775 846 ? 5 316 448 548 632 705 775 ? 4 282 400 490 564 632 692 CAPITAL 3 245 346 423 490 548 600 ? 2 200 282 346 400 448 490 ? 1 141 200 245 282 316 346 ? 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 ? LABOR ? ? ? ? ? Table 7-4 shows a production relationship. Assuming the capital stock is fixed at three units and the cost per day of labor is $65, what is the most labor that it is efficient to hire if the product price is $1 per unit?
A. 2 B. 3 C. 4 D. 5
The property that rules out indifference curves that cross is:
A. independence. B. completeness. C. diminishing marginal rate of substitution. D. transitivity.
A natural monopoly
A) has one lowest-cost producer in the industry. B) exists only when it is regulated. C) has long-run average costs equal to zero. D) always experiences diseconomies of scale.