In a Stackelberg oligopoly
A) the leader moves first, and the follower chooses its price in the second stage of the game.
B) the leader moves first, and the follower chooses its output in the second stage of the game.
C) both firms act simultaneously, but one chooses price and the other output level.
D) there is no Nash equilibrium.
Ans: B) the leader moves first, and the follower chooses its output in the second stage of the game.
You might also like to view...
What is the natural rate hypothesis?
What will be an ideal response?
In the example of the peg between Britain and Germany, what would have been the case if Britain had adhered to the pegged exchange rate?
A) It would not have had the option of raising its own rate. B) It would have been able to inflate its currency to keep output stable. C) It would not have been able to inflate its currency to keep output stable. D) It would have had to raise taxes and balance its budget.
The inability of Congress to pass a stimulus package after September 11, 2001, could be used as an argument for
A. activist fiscal policy. B. activist monetary policy. C. expansionary fiscal policy. D. contractionary monetary policy.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 2.5 below to answer the question(s) that follow.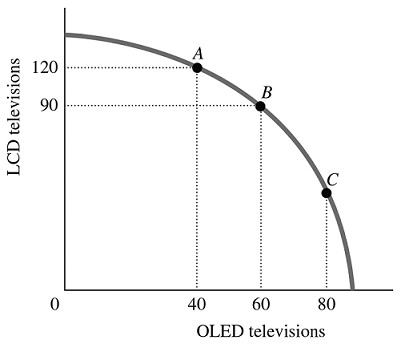 Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. For this economy to move from Point C to Point B, ________ additional LCD TVs could be produced when the production of OLED TVs is reduced by 20.
Figure 2.5Refer to Figure 2.5. For this economy to move from Point C to Point B, ________ additional LCD TVs could be produced when the production of OLED TVs is reduced by 20.
A. exactly 30 B. exactly 60 C. fewer than 30 D. more than 30