Assume that the nominal exchange rate increases by 2%. If prices (both domestic and foreign do not change), we know that
A) domestic goods are now relatively cheaper.
B) domestic goods are now relatively more expensive.
C) foreign goods are now relatively cheaper.
D) both B and C
D
You might also like to view...
Why are income taxes on capital income more powerful than those on labor income?
What will be an ideal response?
Refer to Figure 9.4. In the short run, how much should the firm produce at the price P3?
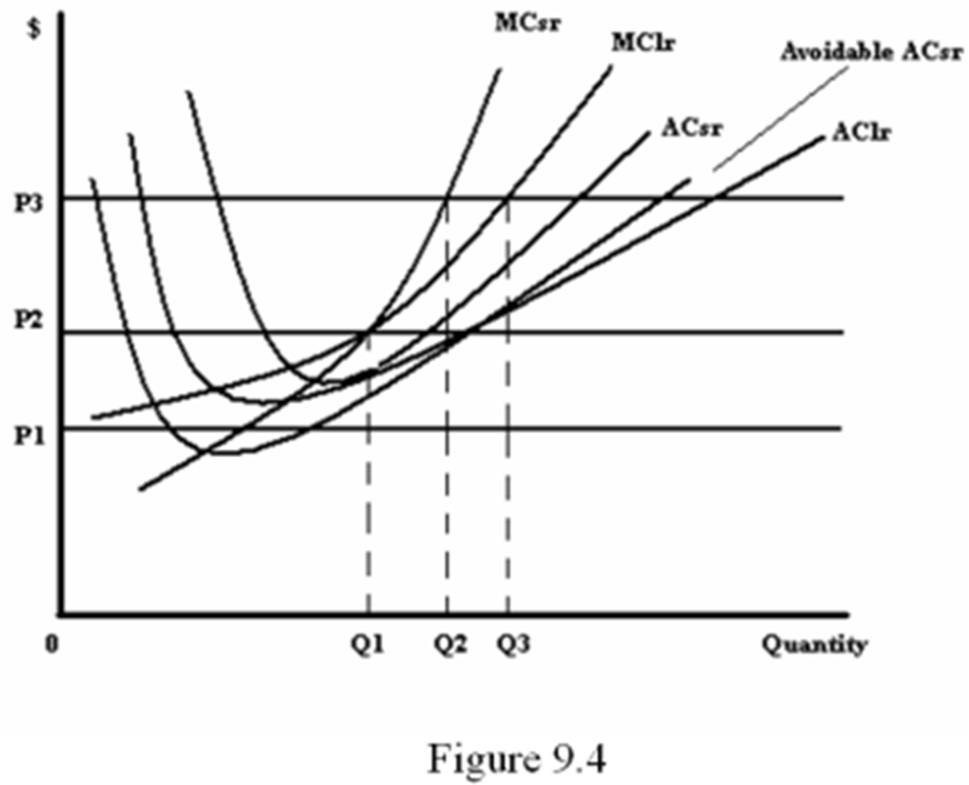
A. 0
B. Q1
C. Q2
D. Q3
Under a floating exchange-rate regime
A. monetary policy must be used to manage the exchange rate. B. the changes in the exchange rate can take care of external balance, leaving macroeconomic policy to take care of internal balance. C. only fiscal policy should be used to reconcile the goals of internal and external balance. D. deficits and surpluses in the official settlements balance will be the primary concern of policy makers.
A technological breakthrough in using photons for computers will increase the productivity of those working with computers a hundredfold. You would expect this breakthrough to shift the
A. labor supply curve up, reducing the quantity of labor demanded at any given real wage. B. labor supply curve down, raising the quantity of labor demanded at any given real wage. C. marginal product of labor curve up and to the right, raising the quantity of labor demanded at any given real wage. D. marginal product of labor curve down and to the left, reducing the quantity of labor demanded at any given real wage.