Refer to the graph below for a purely competitive firm. When the firm is in equilibrium in the short run, the amount of economic profit per unit is:
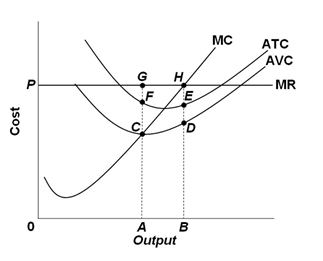
A. EH
B. DE
C. DH
D. DB
A. EH
You might also like to view...
A current account surplus
A) poses a problem if domestic savings are being invested more profitably abroad than they would be at home. B) may pose no problem if domestic savings are being invested more profitably abroad than they would be at home. C) may pose no problem if domestic savings are being invested less profitably abroad than they would be at home. D) there is no relation between current account surplus and between savings and investment. E) poses a problem if domestic savings are being invested less profitably abroad than they would be at home.
The nominal GDP of Year 2 is
A) $800. B) $1050. C) 1900. D) $2400.
A primary difference between rebates and coupons?
A) Coupons allow individuals to sort themselves into the high-elasticity group after the sale. B) Neither coupons or rebates are redeemed in high numbers. C) Rebates allow individuals to sort themselves into the high-elasticity group after the sale. D) Coupons are legal and rebates are illegal.
During the last two centuries, after adjustment for inflation,
a. corporate bonds have yielded a real return of approximately 7 percent annually, compared to a real return of about 3 percent for corporate stocks. b. corporate stocks have yielded a real return of approximately 7 percent annually, compared to a real return of about 3 percent for bonds. c. both corporate stocks and bonds have yielded a real rate of return of about 3 percent. d. both corporate stocks and bonds have yielded a real rate of return of about 7 percent.