Explain Paul Romer's ideas concerning economic growth
What will be an ideal response?
Romer argues that knowledge is a factor of production just as capital and labor are. Economies must invest in education as they do in capital. Past investments in capital make it profitable to acquire more knowledge, implying that investment leads to new knowledge that leads to new investment. There can be an investment-knowledge cycle that continually stimulates economic growth. According to Romer, ideas drive economic growth.
You might also like to view...
If corn and soybean are alternative crops grown by most farmers, an increase in the price of corn, other things constant, is likely to:
a. increase the supply of corn. b. ?increase the supply of soybeans. ? c. decrease the supply of soybeans. ? d. decrease the supply of corn. ? e. decrease the demand for soybeans.
The statistical details on the U.S. balance of international payments between 1790 and 1860 help economic historians determine
(a) what the U.S. sold domestically. (b) how other countries paid for their own domestic goods and services. (c) how the U.S. paid other countries for their exports. (d) changes in domestic trade patterns.
Antitrust laws allow the government to
a. collect revenues through the antitrust tax. b. break up companies. c. purchase privately-held companies through eminent domain. d. All of the above are correct.
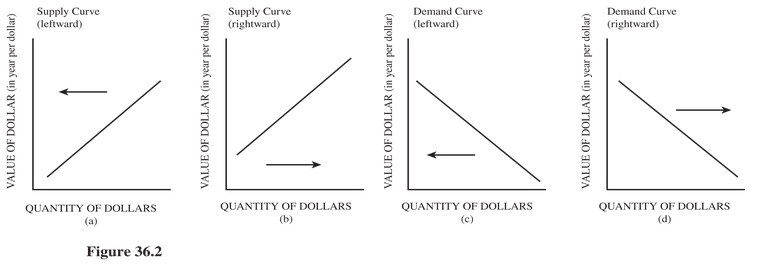 Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation, ceteris paribus: The U.S. economy suddenly experiences a recession.
Choose the letter of the diagram in Figure 36.2 that represents the shift in the foreign exchange market for dollars given the following situation, ceteris paribus: The U.S. economy suddenly experiences a recession.
A. a. B. b. C. c. D. d.