Assuming all else equal, if the real interest rate increases, it will lead to:
A) a decrease in the quantity of credit demanded by a firm.
B) a rightward shift of the credit demand curve of a firm.
C) a leftward shift of the credit demand curve of a firm.
D) an increase in the quantity of credit demanded by a firm.
A
You might also like to view...
Each of the following is an example of discretionary fiscal policy, except
A. public works programs. B. changing tax rates. C. changes in the level of government spending. D. unemployment insurance benefits.
With price? discrimination, a monopoly
A) converts consumer surplus into economic profit.
B) converts producer surplus into economic profit.
C) can charge a single price to all customers.
D) produces less output than if it does not price discriminate.
E) converts consumer surplus into dead weight loss.
Unlike a private good, a public good:
A. has no opportunity costs. B. has benefits available to all, including nonpayers. C. produces no positive or negative externalities. D. is characterized by rivalry and excludability.
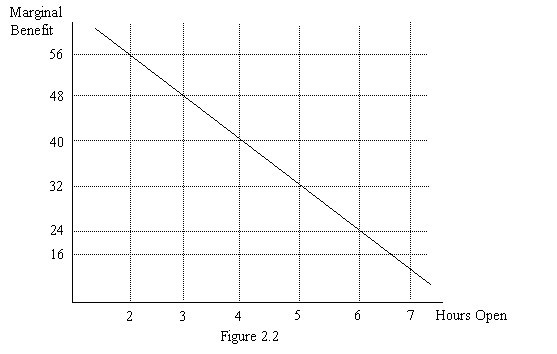 Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Joe staying open 6 hours per day. If he is following the marginal principle, what must his marginal cost per hour be?
Joe runs a business and needs to decide how many hours to stay open. Figure 2.2 illustrates his marginal benefit of staying open for each additional hour. Suppose that we observe Joe staying open 6 hours per day. If he is following the marginal principle, what must his marginal cost per hour be?
A. $16 B. $24 C. $32 D. $48