Assume that the government increases spending and finances the expenditures by borrowing in the domestic capital markets. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a flexible exchange rate system, what happens to the GDP Price Index and reserve-related (central bank) transactions in the context of the Three-Sector-Model?
a. The GDP Price Index falls, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same.
b. The GDP Price Index and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same.
c. The GDP Price Index falls, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions become more negative (or less positive).
d. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
e. The GDP Price Index rises, and reserve-related (central bank) transactions remain the same.
.E
You might also like to view...
Refer to the table below. If at the current advertising level, A = $10,000, B = $15,000, and C = $8,000, to maximize profit, which of the following should the firm do?
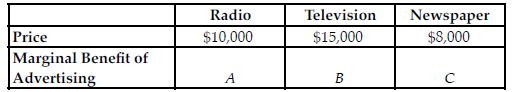
The table above shows the current costs for a firm to advertising on the radio, television, and newspaper.
A) The firm should decrease its advertising on the radio and increase its advertising in newspapers.
B) The firm has optimally allocated their advertising budget, but that does not guarantee that they have maximized their profits.
C) The firm should decrease its advertising on the radio and increase its advertising on television.
D) The firm has optimally allocated their advertising budget, which guarantees they have maximized their profits.
Why is it that projects that have negative net present values are sometimes undertaken?
What will be an ideal response?
If the Congress passes legislation to cut taxes to counter the effects of a severe recession, then this would be an example of a:
a. Nondiscretionary fiscal policy b. Contractionary fiscal policy c. Political business cycle d. Expansionary fiscal policy
Constant returns to scale implies that if N and K both increase by 3% that
A) output (Y) will increase by 3%. B) Y/N will increase by 3%. C) Y/N will increase by less than 3%. D) the capital-labor ratio will increase by 3%.