The minimum water-cement ratio for complete hydration of Portland cement is approximately 0.4. However, we generally need a larger w- c ratio in concrete mixes. Why is that so, and what is the effect of greater-than-minimum w-c ratio?
What will be an ideal response?
A w-c ratio > 0.4 is required to obtain concrete with required slump so that it can work its way into the formwork around steel reinforcement. A larger w-c ratio weakens the concrete.
You might also like to view...
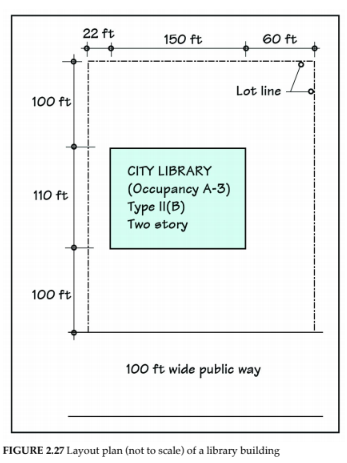
Is a university or a college campus building included in "Educational" occupancy? Explain your answer.
________: reflects what a $1 today would have purchased in goods and services in a particular base period.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The latitude at the equator is 90°
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Solution 19.27 Repeat Problem 19.26, except use the normal distribution for the CFAT in years 7 through 10 with an expected value of $2 million and a standard deviation of $500,000.
Problem 19.26
Jennifer, a senior project manager, estimated net cash flow after taxes (CFAT) for a large project she is working on. The additional CFAT of $2,800,000 in year 10 is the salvage value, estimated at 9% of the $31 million first cost for all capital assets.
 FIGURE 1.png)
The PW value at the current MARR of 7% per year is
PW = ?31,000 + 5400(P?A,7%,6) + 2040(P?A,7%,4)(P?F,7%,6) + 2800(P?F,7%,10) = $767
Jennifer believes the MARR will vary over a relatively narrow range, as will the CFAT, especially during the out years of 7 through 10. She is willing to accept the other estimates as certain. Use the following probability distribution assumptions for MARR and CFAT to perform a simulation—hand- or spreadsheet-based.
MARR. Uniform distribution over the range 6% to 10%.
CFAT, years 7 through 10. Uniform distribution over the range $1,600,000 to $2,400,000 for each year.
Plot the resulting PW distribution. Should the plan be accepted using decision making under certainty? Under risk?