The effects of allometric growth on head morphology in the human and chimpanzee
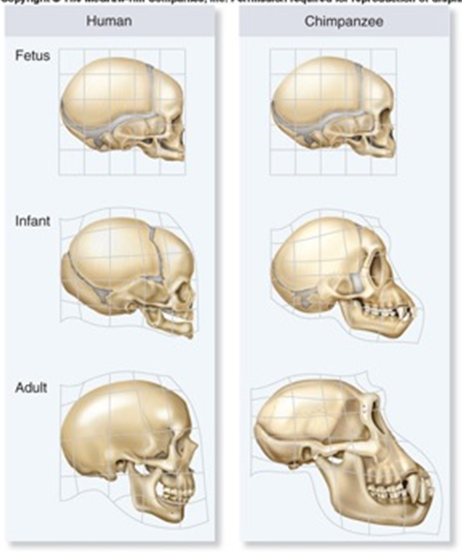
A. The human and chimp fetal skull are exactly the same, the human jaw development slows down after adulthood.
B. Heterochrony is occurring, the chimp jaws continue to develop at a faster rate than human jaws.
C. Paedomorphosis is occurring, the human jaw retains its small size while the chimp jaw continues to grow even in adulthood.
D. The nasal passages of the chimp are shortened due to reduced growth during fetal development while the nasal passages of the human grow through adulthood.
E. All of the choices are correct.
B. Heterochrony is occurring, the chimp jaws continue to develop at a faster rate than human jaws.
You might also like to view...
A limiting factor for viral infection is
A. internal metabolic temperature of the host cell. B. nutrition of the host cell. C. stage of cell cycle of the host cell. D. presence of specific receptor molecules on the host cell.
As observed in animal stem cells, plant stem cells are able to
A. exist as mature cells. B. produce nutrients for other cells. C. remain undifferentiated but can divide to produce cells that generate new tissues. D. fight microbial invaders by becoming mobile and phagocytic.
Rabbits introduced to Australia overpopulated because in their new habitat ____
a. people rarely hunted them b. they had no natural diseases c. they had no natural predators d. their food supply was larger e. there were few herbivorous competitors
A requirement of cladistics is that a grouping must include ________.
A. a common ancestor and all its descendants B. species that can interbreed C. species with shared traits D. only living species