The main reason for building large optical telescopes on Earth's surface is
a. that there is a lot of money in science that needs to get spent.
b. to collect as much light as possible from faint objects.
c. to nullify the blurring effects of the Earth's atmosphere and thus produce higher resolution images.
d. to bring astronomical objects closer to make them brighter.
e. that the warm temperatures of the Earth's surface allow for easier telescope operation.
b
You might also like to view...
Solar prominences have twisted and looped shapes because of the solar magnetic field
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
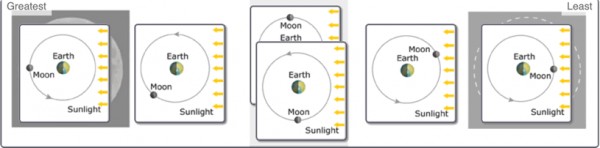
The following figures show a top view of Earth, sunlight, and six different positions of the Moon as it orbits Earth. Note that the distances shown are not drawn to scale. Rank each of the six lunar positions from left to right based on the amount of the Moon’s illuminated surface that is visible from Earth, from greatest to least. (If two diagrams have an equal amount of illumination as seen from Earth, put one on top of the other.)
This diagram shows several stages in a computer simulation of a collision between two galaxies. What is being simulated?
A) Two spiral galaxies merge to become an elliptical galaxy surrounded by debris. B) Two elliptical galaxies merge to become a spiral galaxy. C) Two galaxies collide, sending their stars flying off into space while their centers merge to become a supermassive black hole. D) Two spiral galaxies collide, ultimately merging to make a larger spiral galaxy.
A doubly charged ion (charge 2e) with velocity 6.9 × 106 m/s moves in a circular path of diameter 60.0 cm in a magnetic field of 0.80 T in a mass spectrometer. What is the mass of this ion? (e = 1.60 × 10-19 C)
A) 8.2 × 10-27 kg B) 4.5 × 10-27 kg C) 11 × 10-27 kg D) 3.3 × 10-27 kg E) 6.7 × 10-27 kg