Using Figure 1 above, if the aggregate demand curve shifts from AD2 to AD3 the result in the short run would be: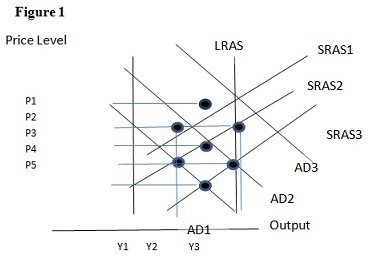
A. P1 and Y2.
B. P2 and Y3.
C. P3 and Y1.
D. P2 and Y2.
Answer: B
You might also like to view...
The average propensity to save (APS) is
A) the difference between the amounts of real disposable income consumed and saved. B) the percentage of additional real disposable income that will go toward real saving. C) the rate at which real savings changes over time. D) the percentage of real disposable income saved.
The quantity of money demanded
A) is infinite. B) is directly controlled by the Fed. C) has no opportunity cost. D) is the quantity that balances the benefit of holding an additional dollar of money against the opportunity cost of doing so. E) changes very infrequently.
Market mechanisms are unlikely to provide
A. prices. B. nonrival goods efficiently. C. supply and demand. D. none of these answer options are correct.
A country with a fixed exchange rate policy and free cross-border capital flows that is experiencing an economic slowdown will find:
A. their central bank will reduce the domestic interest rate in order to fend off the slowdown. B. monetary policy in not available as an economic stabilization tool. C. their corporate equities will become more attractive to foreign investors. D. their currency will depreciate to stimulate exports.