The classic example used to discuss the problem of adverse selection is:
A. fruit and produce markets, such as lemons.
B. drivers with insurance who tend to drive more recklessly.
C. the imbalance of information that exists between a buyer and seller of a used car.
D. workers who shirk when their effort isn't closely monitored.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
In theory, a corrective tax _____ the _____ will create the optimal result
a. equal to; externality b. above; externality c. equal to; price d. above; price
Your teacher decides to play a game where every student must contribute a dollar. All money collected is distributed at the end of the game among the students. This is an example of a
A) positive-sum game. B) zero-sum game. C) strategy. D) negative-sum game.
A consequence of imposing a price floor is that
a. the new price (or price floor) is below the old equilibrium price b. an excess supply of the good is created at the floor price c. an excess demand for the good is created at the floor price d. the supply of the good decreases e. the demand for the good increases
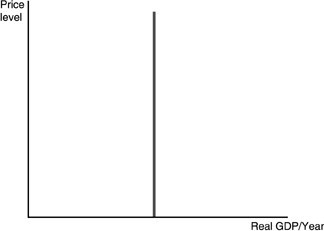 The curve in the above figure will shift to the right when
The curve in the above figure will shift to the right when
A. the proportion of the population that is elderly increases. B. population falls. C. labor productivity increases. D. the price level falls.